Communication Between WCF Service and Android Client
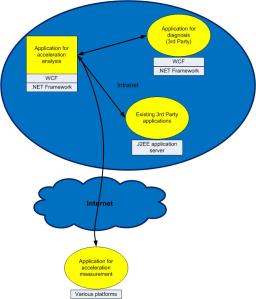 Overview of REST in WCF
Overview of REST in WCFWindows Communication Foundation (WCF), part of the .NET Framework, provides the first unified programming model for rapidly building service-oriented applications. It enables the development of secure, reliable, transacted services that interoperate with current Microsoft investments and non-Microsoft platforms.
With the .NET Framework 3.5 release, WCF added support for building REST style services. REST, an architectural style for building distributed hypermedia driven applications, involves building resource-oriented services by defining resources that implement uniform interfaces using standard HTTP verbs (GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE), and that can be located/identified by a URI.
REST support within WCF was enhanced with the release of .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 to add make REST development easier and to support the ADO.NET Entity Framework entities in WCF contracts. Improvements were made around UriTemplate flexibility and the Visual Studio tooling to increase developer productivity.
Code example
A good tutorial on how to create RESTful Service using Visual Studio can be found here.
First we need to define the structure (class) which will be used for data exchange between server and client. In this case I created a base class named Response and extended classes named ActivityStatusResponse and ConnectionStatusResponse:
public class Response
{
private bool successful;
private string comment;
public bool Successful
{
get
{
return successful;
}
set
{
successful = value;
}
}
public string Comment
{
get
{
return comment;
}
set
{
comment = value;
}
}
}
public class ActivityStatusResponse : Response
{
private string activity;
public string Activity
{
get
{
return activity;
}
set
{
activity = value;
}
}
}
Next we need to define the methods, message formats and URI templates in the interface:
[WebGet(ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Json, UriTemplate = “/{strSessionString}/activityStatus”)]
ActivityStatusResponse GetActivityStatus(string strSessionString);[OperationContract]
[WebGet(ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Json,
UriTemplate = “/{strSessionString}/time={time}&lat={latitude}&long={longitude}”)]
Response StoreLocation(string strSessionString, string time, string latitude, string longitude);
WebMessageFormat parameter defines the data exchange format. In this example JSON format is used.
UriTemplate parameter defines the URI template.
The parameters within curly braces represent variable values. Everything else in the URI (not enclosed within curly braces) is considered a static part of the URI.
After the definition we have to implement the methods. The following code shows the implementation of StoreAcceleration method:
public Response StoreAcceleration(string strSessionString, string strMeasurementTime, string strAccelerationX, string strAccelerationY, string strAccelerationZ)
{
SQLWorks sqlWorks = new SQLWorks();
Response response = new Response();
try
{
string strTime = strMeasurementTime.Replace("_", " ");
DateTime measurementTime = DateTime.ParseExact(strTime, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:fff", null);
double accelerationX = Convert.ToDouble(strAccelerationX.Replace(".", ","));
double accelerationY = Convert.ToDouble(strAccelerationY.Replace(".", ","));
double accelerationZ = Convert.ToDouble(strAccelerationZ.Replace(".", ","));
sqlWorks.StoreAcceleration(strSessionString, measurementTime, accelerationX, accelerationY, accelerationZ);
response.Successful = true;
response.Comment = "Stored!";
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
string sDummy = ex.ToString();
response.Comment = "an error occured!";
response.Successful = false;
}
return response;
}
The service Endpoint and other properties are defined in .config file:
<system.web>
<compilation debug=”true”>
</compilation>
<system.servicemodel>
<bindings>
<webhttpbinding>
<binding name=”DefaultBinding”>
</binding>
</webhttpbinding>
<behaviors>
<endpointbehaviors>
<behavior name=”RESTFriendly”>
<webhttp>
</webhttp>
<behavior name=”RESTServer.JsonServiceAspNetAjaxBehavior”>
<enablewebscript>
</enablewebscript>
</behavior>
<servicebehaviors>
<behavior name=”RESTFriendly”>
<servicemetadata httpgetenabled=”true”>
<servicedebug includeexceptiondetailinfaults=”false”>
</servicedebug>
</servicemetadata>
</behavior>
<services>
<service name=”RESTServer.GaitLinkService”>
<endpoint address=”” behaviorconfiguration=”RESTFriendly” binding=”webHttpBinding” bindingconfiguration=”DefaultBinding” contract=”RESTServer.IGaitLinkService”>
<identity>
<dns value=”localhost”>
</dns>
</identity>
</endpoint>
</service>
<servicehostingenvironment aspnetcompatibilityenabled=”true”>
</servicehostingenvironment>
</services></servicebehaviors></behavior></endpointbehaviors></behaviors></bindings></system.servicemodel></system.web></configuration>
At this point everything is ready to host the service in the windows application:
public void StartRestService()
{
try
{
WebHttpBinding binding = new WebHttpBinding();
RESTServiceHost = new ServiceHost(typeof(GaitLinkService), new Uri("http://localhost:8000/GaitLink"));
RESTServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(typeof(IGaitLinkService), binding, "GaitLink");
RESTServiceHost.Open();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
string sDummy = ex.ToString();
//TODO: notify user about the error!
}
}
Client application
On client side there is a service called CommunicationService and additional class RestClient. Function arguments are sent to the server by generating the url address which has to be the same format as the template specified in the service interface on the server side.
Class RestClient.java:
package com.client.gaitlink;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import android.util.Log;
public class RestClient {
private static String loginParameters;
private static String accelerationParameters;
private static String activityRequestParameters;
private static String locationParameters;
private static String serviceAddress = "http://76.30.178.213:8000/GaitLink/";
private static String convertStreamToString(InputStream is) {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String line = null;
try {
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line + "\n");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void connect(String url) {
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(url);
//HttpPost httppost = new HttpPost(url);
HttpResponse response;
try {
response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
Log.i("REST:Response Status line", response.getStatusLine().toString());
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
InputStream instream = entity.getContent();
String result = convertStreamToString(instream);
Log.i("REST: result", result);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(result);
Log.i("REST", "<jsonobject>\n" + json.toString()
+ "\n</jsonobject>");
// Parsing
JSONArray nameArray = json.names();
JSONArray valArray = json.toJSONArray(nameArray);
for (int i = 0; i < valArray.length(); i++) {
Log
.i("REST", "<jsonname" + i + ">\n"
+ nameArray.getString(i) + "\n</jsonname"
+ i + ">\n" + "<jsonvalue" + i + ">\n"
+ valArray.getString(i) + "\n</jsonvalue"
+ i + ">");
}
json.put("sample key", "sample value");
Log.i("REST", "<jsonobject>\n" + json.toString()
+ "\n</jsonobject>");
instream.close();
}
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (JSONException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public class Response
{
public boolean isSuccessful() {
return successful;
}
public void setSuccessful(boolean successful) {
this.successful = successful;
}
public String getComment() {
return comment;
}
public void setComment(String comment) {
this.comment = comment;
}
private boolean successful;
private String comment;
public Response()
{
this(false, null);
}
public Response(boolean successful, String comment)
{
this.successful = successful;
this.comment = comment;
}
}
public class LoginResponse extends Response
{
private String strSessionString;
public LoginResponse()
{
this(false, null, "LoginFailed");
}
public LoginResponse(boolean successful, String strSessionString, String comment)
{
super(successful, comment);
this.strSessionString = strSessionString;
}
public String getStrSessionString() {
return strSessionString;
}
public void setStrSessionString(String strSessionString) {
this.strSessionString = strSessionString;
}
}
public class ActivityStatusResponse extends Response
{
private String activity;
public String getActivity() {
return activity;
}
public void setActivity(String activity) {
this.activity = activity;
}
public ActivityStatusResponse(boolean successfull, String activity, String comment)
{
super(successfull, comment);
this.activity = activity;
}
public ActivityStatusResponse()
{
this(false, null, "activity request failed");
}
}
private static void SetLoginParameters(String username, String password)
{
loginParameters = "Login?username=" + username + "&password=" + password;
}
public LoginResponse Login(String username, String password)
{
SetLoginParameters(username, password);
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(serviceAddress + loginParameters);
HttpResponse response;
LoginResponse loginResponse = null;
try
{
response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if(entity != null)
{
InputStream instream = entity.getContent();
String result = convertStreamToString(instream);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(result);
// Parsing
JSONArray nameArray = json.names();
JSONArray valArray = json.toJSONArray(nameArray);
loginResponse = new LoginResponse(valArray.getBoolean(1), valArray.getString(0), valArray.getString(2));
instream.close();
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
loginResponse = new LoginResponse();
String sDummy = e.toString();
}
return loginResponse;
}
public Response SendAccelerations(String sSession, String measurementTime, double ax, double ay, double az)
{
setAccelerationParameters(sSession, measurementTime, ax, ay, az);
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(serviceAddress + accelerationParameters);
HttpResponse response;
Response accelerationResponse = null;
try
{
response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if(entity != null)
{
InputStream instream = entity.getContent();
String result = convertStreamToString(instream);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(result);
// Parsing
JSONArray nameArray = json.names();
JSONArray valArray = json.toJSONArray(nameArray);
accelerationResponse = new Response(valArray.getBoolean(0), valArray.getString(1));
instream.close();
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
accelerationResponse = new Response();
String sDummy = e.toString();
}
return accelerationResponse;
}
private static void setAccelerationParameters(String sSession, String measurementTime, double ax, double ay, double az)
{
accelerationParameters = sSession + "/measurementTime=" + measurementTime + "&accelerationX=" + ax + "&accelerationY=" + ay + "&accelerationZ=" + az;
accelerationParameters = accelerationParameters.replaceAll(" ", "_");
}
public Response SendLocation(String sSession, String locationTime, double latitude, double longitude)
{
setLocationParameters(sSession, locationTime, latitude, longitude);
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(serviceAddress + locationParameters);
HttpResponse response;
Response locationResponse = null;
try
{
response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if(entity != null)
{
InputStream instream = entity.getContent();
String result = convertStreamToString(instream);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(result);
// Parsing
JSONArray nameArray = json.names();
JSONArray valArray = json.toJSONArray(nameArray);
locationResponse = new Response(valArray.getBoolean(0), valArray.getString(1));
instream.close();
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
locationResponse = new Response();
String sDummy = e.toString();
}
return locationResponse;
}
private static void setLocationParameters(String sSession, String locationTime, double latitude, double longitude)
{
///{strSessionString}/time={time}&lat={latitude}&long={longitude}
locationParameters = sSession + "/time=" + locationTime + "&lat=" + latitude + "&long=" + longitude;
locationParameters = locationParameters.replaceAll(" ", "_");
}
public ActivityStatusResponse GetActivity(String sSession)
{
setActivityRequestParameters(sSession);
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(serviceAddress + activityRequestParameters);
HttpResponse response;
ActivityStatusResponse activityStatusResponse = null;
try
{
response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if(entity != null)
{
InputStream instream = entity.getContent();
String result = convertStreamToString(instream);
JSONObject json = new JSONObject(result);
// Parsing
JSONArray nameArray = json.names();
JSONArray valArray = json.toJSONArray(nameArray);
activityStatusResponse = new ActivityStatusResponse(valArray.getBoolean(0), valArray.getString(1), valArray.getString(2));
instream.close();
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
activityStatusResponse = new ActivityStatusResponse();
String sDummy = e.toString();
}
return activityStatusResponse;
}
private static void setActivityRequestParameters(String sSession)
{
activityRequestParameters = "/" + sSession + "/activityStatus";
}
}</pre>
</div>
<div>
RestClient methods are called from CommunicationService class. The following example shows the method which retrieves the activity status:
</div>
<div>
<pre id="bt_plainText">private void requestActivity()
{
try
{
if(strSessionString != null)
{
ActivityStatusResponse response = restClient.GetActivity(strSessionString);
connectionAvailable = response.isSuccessful();
strActivity = response.getActivity();
if(strActivity != null && strActivity != "")
{
announceActivityStatus();
}
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
connectionAvailable = false;
}
}
References A Guide to Designing and Building RESTful Web Services with WCF 3.5 Windows Communication Foundation Architecture What Is Windows Communication Foundation?
Hello! Nice job here 🙂
Can you post the source code also?
Moreover, players can play for free and for real money without any difficulties or problems in receiving the money.
You no longer can remove these troublesome programs
from your computer, you do not have the permissions to see them, and you certainly don’t have the permissions to manipulate them. For the GPA customers information – you can move your Great Plains Accounting database from such platforms as Novell, Windows NT, Windows 2000 to Windows 2003 Server or even to Windows 2008 (we are in process of testing for this option, please check with us in few months, currently we are in February 2010).
Good day I am so thrilled I found your website, I really found
you by accident, while I was researching on Google
for something else, Anyways I am here now and would just like to say many thanks
for a remarkable post and a all round interesting blog (I also
love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read it all at the moment but I have bookmarked it and also added in your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a great deal more, Please do keep up the great work.